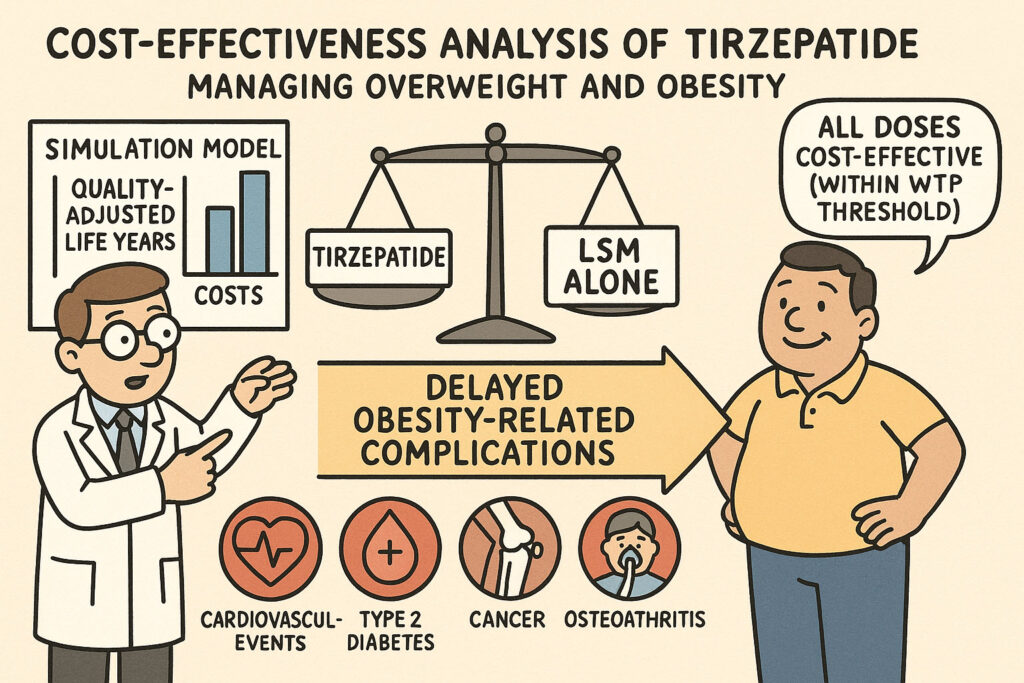
This academic article presents a cost-effectiveness analysis of tirzepatide, a medication for managing overweight and obesity, comparing it against lifestyle modification (LSM) alone. Researchers used a simulation model to project lifetime health outcomes and costs for patients, focusing on complications like cardiovascular events, type 2 diabetes, cancer, osteoarthritis, and sleep apnea. The study concluded that all tested doses of tirzepatide were cost-effective alternatives to LSM, falling within accepted willingness-to-pay thresholds for quality-adjusted life years (QALYs) gained. The analysis highlights that tirzepatide significantly delays the onset of obesity-related complications, especially cardiovascular disease and type 2 diabetes, ultimately improving patient health over their lifetime despite higher initial treatment costs.
Audio Overview (Google NotebookLM)
(26 minutes 04 seconds)

