Oncobesity News Posts
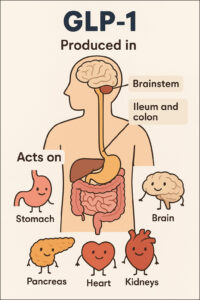
Where is GLP-1 is produced and where in the body does it act?
The provided text describes glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1), detailing its production and the wide array of organs and systems it affects. Primarily, GLP-1 is generated in the intestinal

⚖️ GLP-1s: Integrating Diet and Activity for Optimal Outcomes
This JAMA article provides comprehensive guidance for clinicians on integrating diet and physical activity when prescribing GLP-1 receptor agonists for weight management. It outlines strategies for monitoring and

⚖️ Navigating GLP-1 Weight Loss: Diet, Exercise, and Well-being
This patient-focused guide from JAMA Internal Medicine provides essential information for individuals utilizing GLP-1 medications for weight loss. It outlines the medications’ functions and offers practical dietary advice through a “MEAL” plan, emphasizing muscle

🧪 Unregulated Additives in Compounded GLP-1 Medications
The practice of compounding pharmacies adding various supplements to GLP-1 receptor agonist formulations like semaglutide or tirzepatide is very common in the United States. These additions, which

⚠️ FDA Failures and GLP-1 Compounding Risks
“FDA Regulatory Failures in Enforcing Limits on GLP-1 Compounding Puts Patients at Risk,” critically examines the Food and Drug Administration’s (FDA) oversight of compounded GLP-1 medications.

🤢 Adiposity and Colorectal Cancer Risk: A Systematic Review
A systematic review investigating the relationship between adiposity measures and the risk of developing colorectal cancer (CRC), building upon existing research that often relies solely on Body Mass

💪 GLP-1s: Diabetes, Weight Loss, and Cancer Reduction
This source explores the impact of semaglutide, a weight loss medication, on muscle mass, glucose regulation, and bone health in adults with obesity. It highlights

💲 Tirzepatide: A Cost-Effective Path to Obesity Management
This academic article presents a cost-effectiveness analysis of tirzepatide, a medication for managing overweight and obesity, comparing it against lifestyle modification (LSM) alone. Researchers used a simulation model to project lifetime health
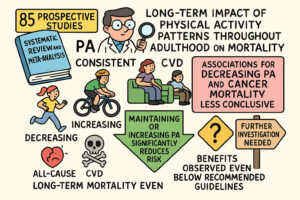
🏃 Physical Activity Trajectories and Mortality: A Meta-Analysis
A systematic review and meta-analysis of 85 prospective studies, examining the long-term impact of physical activity (PA) patterns throughout adulthood on mortality. The authors aimed to understand how consistent, increasing,
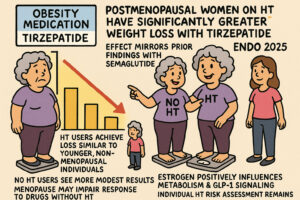
Hormone Therapy Enhances Tirzepatide Weight Loss in Menopause
The source discusses research indicating that postmenopausal women on hormone therapy (HT) experience significantly greater weight loss when treated with tirzepatide, an obesity medication, compared

⚖️ The History of Obesity
The provided text offers a comprehensive overview of how obesity has been understood and depicted across different historical periods, from ancient civilizations to the present day. It traces

👨⚕️ AI-Driven Virtual Human for GP Obesity Training
This document presents a pilot feasibility study published in “Obesity Science & Practice” that investigates the effectiveness of an AI-driven Virtual Human (VH) intervention designed to enhance General Practitioner (GP)

👵 Ozempic Face: GLP-1 and Aesthetic Surgery
This scholarly article from Aesthetic Surgery Journal Open Forum discusses the phenomenon of “Ozempic Face,” a term used to describe the accelerated facial aging and volume loss experienced by some patients

✨ GLP-1s and Post-Weight Loss Plastic Surgery Trends
There is growing evidence—especially in the plastic surgery community—that the recent surge in GLP‑1 medications (like Ozempic, Wegovy, Mounjaro) for weight loss is fueling a

💉 Counterfeit Ozempic: FDA Warns of Unsafe Drug Supply (4/14/2025)
The provided text, originating from the Food and Drug Administration (FDA), serves as a crucial public health warning regarding counterfeit Ozempic (semaglutide) injections found within the U.S. drug

Obesity Treatment Outcomes with Semaglutide or Tirzepatide
This original research article examines the real-world effectiveness of semaglutide and tirzepatide for obesity treatment, focusing on how medication discontinuation impacts weight loss and glycemic control. The retrospective cohort study analyzed electronic health records from

Unpacking the GLP-1 Gold Rush
We ask experts for their views on the GLP-1 market in this exclusive eBook. GLP-1 receptor agonists have rapidly evolved from niche diabetes drugs to
Your Weight Matters Region
Your Weight Matters Regional is traveling the country, bringing expert-led education and practical guidance to cities near you. These FREE half-day events are designed to
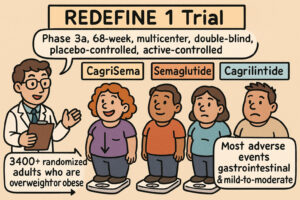
CagriSema: Weight Loss in Overweight or Obese Adults
This document details a Phase 3a, 68-week, multicenter, double-blind, placebo-controlled, and active-controlled clinical trial (REDEFINE 1) investigating the efficacy and safety of cagrilintide–semaglutide (CagriSema) for weight loss in adults
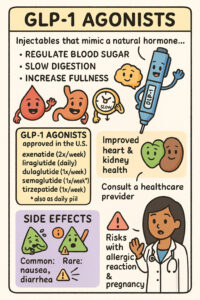
GLP-1 Agonists: Uses, Mechanism, and Side Effects
https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/treatments/13901-glp-1-agonists The provided text from the Cleveland Clinic offers a comprehensive overview of GLP-1 agonists, a class of medications primarily used to manage Type 2 diabetes and obesity. It explains how these

Orforglipron for Early Type 2 Diabetes Management
This scientific paper presents the ACHIEVE-1 trial, a phase 3 study investigating orforglipron, an oral, nonpeptide GLP-1 receptor agonist, for treating type 2 diabetes. The research evaluates its efficacy

ADA (American Diabetes Association) June 20-23 Obesity Medicines – Other Posters and Talks
🧪 NA‑931 (Bioglutide™) – Biomed Industries, Inc.Presentation (Oral):Title: “Phase 2 Clinical Trials of NA‑931, an Oral Novel Quadruple IGF‑1, GLP‑1, GIP, and Glucagon Receptor Agonist,

Tirzepatide for Weight Loss in Non-Diabetics: A Meta-Analysis
Kommu S, Sharma PP, Gabor RM. Efficacy and Safety of Tirzepatide on Weight Loss in Patients Without Diabetes Mellitus: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of

Wikipedia and the Weight Loss Drugs
Wikipedia is a free, multilingual, web-based, and openly editable encyclopedia maintained by a global community of volunteers. It’s hosted by the non-profit Wikimedia Foundation. Wikipedia offers articles on
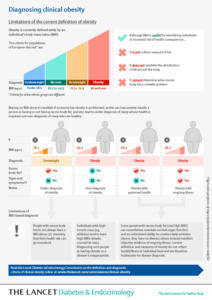
Defining Clinical Obesity
Definition and diagnostic criteria of clinical obesityRubino, Francesco et al.The Lancet Diabetes & Endocrinology, Volume 13, Issue 3, 221 – 262 The Lancet Diabetes & Endocrinology
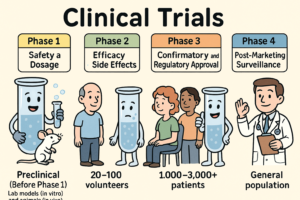
What are Clinical Trials and why do we need them?
Clinical trials are carefully designed research studies conducted in humans to evaluate the safety, efficacy, and overall benefit of medical interventions such as drugs, biologics,

What is “Enforcement Discretion” (FDA context)?
Enforcement discretion means that a regulatory agency like the FDA (U.S. Food and Drug Administration) chooses not to enforce certain rules or regulations under specific

Retatrutide: A Triple Agonist for Diabetes and Obesity
Abdul-Rahman T, Roy P, Ahmed FK, Mueller-Gomez JL, Sarkar S, Garg N, Femi-Lawal VO, Wireko AA, Thaalibi HI, Hashmi MU, Dzebu AS, Banimusa SB, Sood

GLP-1 Agonists and Neurological Adverse Events in FAERS
Chen H, Liu S, Gao S, Shi H, Yan Y, Xu Y, Fang J, Wang W, Chen H, Liu Z. Pharmacovigilance analysis of neurological adverse
Camurus: Advancing Patient Care Through Innovation with FluidCrystal®
Drug delivery for incretins refers to how medications that mimic or enhance the activity of incretin hormones—primarily GLP-1 (glucagon-like peptide-1) and GIP (glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide)—are

The Quantum Power of GLP-1 Peptides: Unlocking the Science that Leads to Lasting Weight Loss and Optimal Healthspan Paperback – June 3, 2025
by William A Seeds MD (Author) ($36.00) In The Quantum Power of GLP-1 Peptides: Unlocking the Science that Leads to Lasting Weight Loss and Optimal Healthspan, Dr. William A.Seeds

Nourishing GLP-1 Therapy for Obesity
This academic article, “Nutritional priorities to support GLP‐1 therapy for obesity,” is a joint advisory from several prominent American health organizations. It examines the use of GLP-1 receptor

MAHA Agenda Excludes GLP-1 Coverage Expansion
PharmaVoice article discusses the Trump administration’s decision not to expand Medicare and Medicaid coverage for GLP-1 obesity drugs, despite their increasing use and the potential for

The Ozempic Era and Shifting Obesity Blame
Schmidt, Laura A., and Luc L. Hagenaars. “The Ozempic Era Could Shift Blame for Obesity From Individuals to Commercial Food Systems.” Issues in Science and Technology 41,

Is Obesity Genetic or Environmental? YES!
Vocabulary-GWAS – A Genome-Wide Association Study – a research method used to identify genetic variations (like single nucleotide polymorphisms or SNPs) associated with a specific

GLP-1 RAs: Psychiatric, Cognitive, and Quality of Life Effects
This meta-analysis examines the impact of Glucagon-Like Peptide 1 Receptor Agonists (GLP1-RAs), medications used for obesity and diabetes, on the mental health and quality of

Novo Nordisk Partners with Telehealth for Wegovy Promotion
May 23, 2025Stat + by Katie Palmer https://ro.co/ https://lifemd.com/ Stat + reports on the evolving landscape of GLP-1 drug marketing, noting a shift in the

Cysteine Deficiency Drives Weight Loss by Depleting CoA
This research paper explores the impact of amino acid restriction on weight loss, focusing on the unique effects of cysteine deficiency. The study demonstrates that cysteine restriction in mice, particularly those with compromised
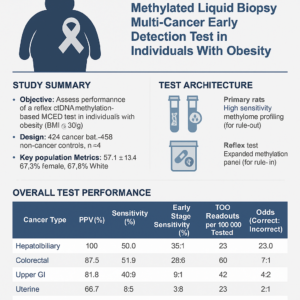
MCED Test Performance in Obese Individuals
This abstract evaluates a multi-cancer early detection (MCED) blood test specifically designed for individuals with obesity, a group at higher risk for several cancers often without standard screening.

Mochi Health Launches Insurance-Based Plans, Expanding Access to Personalized Obesity Care with Behavioral Therapy
What You Should Know: – Mochi Health, a physician-guided obesity care program, announced the launch of its new insurance-based plans. – These expanded offerings are
